Explore the Contents
- 1 What Is Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)?
- 1.1 Dialectical Behavior Therapy Techniques
- 1.2 What Dialectical Behavioral Therapy Can Help With
- 1.3 Benefits of Dialectical Behavioral Therapy
- 1.4 Effectiveness of Dialectical Behavior Therapy
- 1.5 Things to Consider About Dialectical Behavior Therapy
- 1.6 How to Get Started With Dialectical Behavior Therapy
What Is Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)?

A modified form of cognitive behavioural therapy is dialectical behaviour therapy (DBT) (CBT). Its main objectives are to teach people how to be present, create healthy coping mechanisms for stress, control their emotions, and enhance interpersonal connections.
DBT has been modified to treat a variety of mental health issues even though it was developed to address borderline personality disorder (BPD). It can benefit those who have trouble controlling their emotions or are engaging in damaging habits (such as eating disorders and substance use disorders). Post-traumatic stress disorder may occasionally be treated with this kind of therapy.
What You Should Know About DBT Therapy
NOTE
| Daniel B. Block, MD, has given this video a medical review. |
Dialectical Behavior Therapy Techniques
DBT has developed into an evidence-based psychotherapy strategy that is applied to the treatment of numerous conditions. Settings where DBT are frequently employed include:
- Patients receive behavioural skill instruction in a group setting during group therapy.
- Individual treatment with a qualified practitioner allows patients to customise newly acquired behavioural skills to their unique set of life circumstances.
- Patients can call the therapist between sessions to receive advice on coping with a challenging situation they are currently in through phone coaching.
The following are just a few of the DBT strategies and techniques.
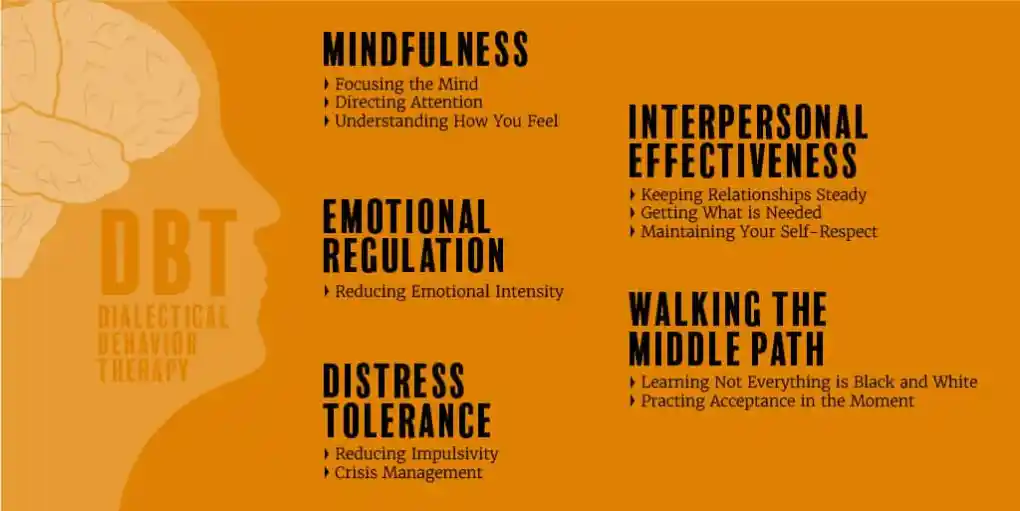
Core Mindfulness
The improvement of mindfulness abilities is a significant benefit of DBT. 4 Living in the moment or focusing on the here and now is made easier by mindfulness. This assists you in developing a nonjudgmental awareness of both what is going on inside of you (your thoughts, feelings, sensations, and impulses) as well as what is going on outside of you (what you see, hear, smell, and touch).
When you are experiencing emotional distress, mindfulness skills can help you slow down and concentrate on employing appropriate coping mechanisms. The technique can also assist you in maintaining your composure and preventing impulsive conduct and automatic negative thought patterns.
Distress Tolerance
Your ability to tolerate stress will help you accept both yourself and your circumstances. DBT offers a number of crisis management methods, such as:
- Distraction
- Enhancing the present
- Self-soothing
- weighing the benefits and drawbacks of not accepting suffering
Techniques for coping with distress help you get ready for strong emotions and give you the tools you need to deal with them in a way that will benefit you in the long run.
NOTE
Sample Exercise: Putting Your Body in Charge
Up and down the steps you go. Go outdoors if you’re inside. If you’re sitting, stand up and take a few steps. By letting your emotions follow your body, you can divert your attention from yourself.
Interpersonal Effectiveness
Your ability to express your needs and say “no” in a relationship and still maintain a positive, healthy relationship depends on your interpersonal effectiveness. You will gain the ability to respect yourself and others, listen and communicate more effectively, and handle difficult people.
Emotion Regulation
You can deal with intense emotions more successfully if you have good emotion control. Your ability to recognise, name, and modify your emotions will be aided by the abilities you acquire.
Stages of DBT
Four stages of treatment are often used to separate dialectical behaviour therapy.
1: The most severe and self-destructive behaviours are addressed first at the start of treatment. This may involve problems like self-harm or suicidal tendencies.
2: Next, the focus of treatment shifts to problems that have an impact on a person’s quality of life, like their capacity for managing their emotions, interpersonal effectiveness, and ability to bear discomfort.
3: The attention now shifts to problems with self-worth and social interactions.
4: At this stage, treatment focuses on assisting patients in making the most of their lives, including identifying strategies for enhancing happiness, preserving relationships, and pursuing their life goals.
What Dialectical Behavioral Therapy Can Help With
When they discovered that cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) alone did not work as well as expected in patients with BPD, Dr. Marsha Linehan and her colleagues created DBT in the late 1980s. To cater to the particular requirements of these people, Dr. Linehan and her team added techniques and created a treatment.
DBT, despite being created with BPD in mind, may work well for treating:
- Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
- Bipolar disorder
- Borderline personality disorder (BPD)
- Eating disorders (such as anorexia nervosa, binge eating disorder, and bulimia nervosa)
- Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
- Major depressive disorder (including treatment-resistant major depression and chronic depression)
- Non-suicidal self-injury
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Substance use disorder8
- Suicidal behavior
Benefits of Dialectical Behavioral Therapy
The goal of DBT is to help the person receiving therapy experience positive changes by resolving the apparent tension between self-acceptance and change. Offering validation is a step in this process that makes people more receptive to cooperation and less prone to feel upset by the prospect of change.
In reality, the therapist validates that a person’s actions “make sense” in light of their unique experiences while not necessarily concurring that they are the best course of action for resolving a problem.
Although each therapeutic setting has its own structure and objectives, group skills training, individual psychotherapy, and phone coaching all share some DBT characteristics.
- Change and acceptance: You’ll discover methods for tolerating your feelings, circumstances in life, and even yourself. Additionally, you will learn abilities that will enable you to alter your conduct and social interactions for the better.
- Behavioral: You’ll learn to identify issues or harmful behaviour patterns and swap them out for more beneficial and productive ones.
- Cognitive: Your attention will be on modifying unhelpful or ineffective thoughts and beliefs.
- Collaboration: will teach you how to work as a team and communicate clearly (therapist, group therapist, psychiatrist).
- You’ll pick up additional powers to improve your skill sets.
- Support: You’ll be prompted to acknowledge and build upon your good traits and strengths.
Effectiveness of Dialectical Behavior Therapy
People who successfully improve their coping skills with the aid of this therapy approach can create efficient means of controlling and expressing intense emotions. Additionally, studies have shown that DBT works for people of any age, sex, gender identity, sexual orientation, or race/ethnicity.
- DBT is effective in treating: Borderline personality disorder (BPD) and lowering the risk of suicide in people with BPD, according to studies. According to one study, more than 75% of BPD patients no longer satisfied the diagnostic criteria for the illness after receiving treatment for a year.
- According to a different study: Interventions that included skills training as a component of treatment seemed to be more effective at lowering suicidality than DBT without skills training.
- DBT may be a useful treatment: For a variety of mental health issues, but most of the research has focused on how well it works for persons with borderline personality disorder who have suicidal and self-harming thoughts. 1 For instance, studies have shown that this kind of therapy appears to be successful in treating PTSD, depression, and anxiety.
Things to Consider About Dialectical Behavior Therapy
DBT demands a considerable time commitment. For those who regularly struggle to keep up with these assignments, this could be difficult.
For some people, using some of the skills can be difficult. People explore traumatic events and emotional pain at various stages of treatment, which can be upsetting.
Can You Do Dialectical Behavior Therapy On Your Own?
To help you learn new coping mechanisms, there are certain activities you can do on your own. For instance, you can use mindfulness, breathing techniques, and progressive muscle relaxation to enhance your capacity to handle distress.
It’s crucial to keep in mind that this shouldn’t be utilised in place of expert advice. It’s always better to seek the assistance of a licenced mental health expert if you’re experiencing mental health issues.
How to Get Started With Dialectical Behavior Therapy
The best way to determine if DBT is the right treatment for you is to speak with a trained professional. To determine if DBT could be a suitable fit, they will examine your symptoms, treatment trajectory, and therapy objectives.
It’s important to speak with a healthcare provider or mental health expert who is knowledgeable about DBT if you believe that you or a loved one might benefit from the treatment. Nevertheless, it’s not always simple to locate DBT therapists.
Linehan to train mental health professionals in DBT). You can use the directory to search by state for clinicians and programmes that have received DBT training from Behavioral Tech, LLC, or the University of Washington’s Behavioral Research and Therapy Clinics.
You can also request a referral to a DBT next expert from your healthcare provider, your current therapist, or another reputable mental health next professional. DBT therapy is also provided by some online therapists.